jaccard¶
Whereas the bedtools intersect tool enumerates each an every intersection between two sets of genomic
intervals, one often needs a single statistic reflecting the similarity of the two sets based on the
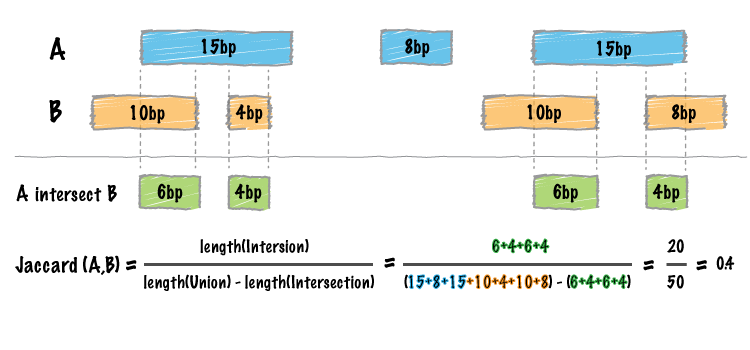
intersections between them. The Jaccard statistic is used in set theory to represent the ratio of the
intersection of two sets to the union of the two sets. Similarly, Favorov et al [1] reported the use
of the Jaccard statistic for genome intervals: specifically, it measures the ratio of the number of
intersecting base pairs between two sets to the number of base pairs in the union of the two sets.
The bedtools jaccard tool implements this statistic, yet modifies the statistic such that the length of the
intersection is subtracted from the length of the union. As a result, the final statistic ranges from 0.0
to 1.0, where 0.0 represents no overlap and 1.0 represent complete overlap.
[1] Exploring Massive, Genome Scale Datasets with the GenometriCorr Package.
Favorov A, Mularoni L, Cope LM, Medvedeva Y, Mironov AA, et al. (2012)
PLoS Comput Biol 8(5): e1002529. doi:10.1371/journal.pcbi.1002529
Note
The jaccard tool requires that your data is pre-sorted by chromosome and
then by start position (e.g., sort -k1,1 -k2,2n in.bed > in.sorted.bed
for BED files).
Usage and option summary¶
Usage:
bedtools jaccard [OPTIONS] -a <BED/GFF/VCF> -b <BED/GFF/VCF>
Option |
Description |
|---|---|
-a |
BED/GFF/VCF file A. Each feature in A is compared to B in search of overlaps. Use "stdin" if passing A with a UNIX pipe. |
-b |
BED/GFF/VCF file B. Use "stdin" if passing B with a UNIX pipe. |
-f |
Minimum overlap required as a fraction of A. Default is 1E-9 (i.e. 1bp). |
-F |
Minimum overlap required as a fraction of B. Default is 1E-9 (i.e., 1bp). |
-r |
Require that the fraction of overlap be reciprocal for A and B. In other words, if -f is 0.90 and -r is used, this requires that B overlap at least 90% of A and that A also overlaps at least 90% of B. |
-e |
Require that the minimum fraction be satisfied for A _OR_ B. In other words, if -e is used with -f 0.90 and -F 0.10 this requires that either 90% of A is covered OR 10% of B is covered. Without -e, both fractions would have to be satisfied.**-s** Force "strandedness". That is, only report hits in B that overlap A on the same strand. By default, overlaps are reported without respect to strand. |
-S |
Require different strandedness. That is, only report hits in B that overlap A on the _opposite_ strand. By default, overlaps are reported without respect to strand. |
-split |
Treat "split" BAM (i.e., having an "N" CIGAR operation) or BED12 entries as distinct BED intervals. |
Default behavior¶
By default, bedtools jaccard reports the length of the intersection, the length of the union (minus the intersection),
the final Jaccard statistic reflecting the similarity of the two sets, as well as the number of intersections.
$ cat a.bed
chr1 10 20
chr1 30 40
$ cat b.bed
chr1 15 20
$ bedtools jaccard -a a.bed -b b.bed
intersection union jaccard n_intersections
5 20 0.25 1
Controlling which intersections are included¶
One can also control which intersections are included in the statistic by requiring a certain fraction of overlap
with respect to the features in A (via the -f parameter) or also by requiring that the fraction of overlap is
reciprocal (-r) in A and B.
$ cat a.bed
chr1 10 20
chr1 30 40
$ cat b.bed
chr1 15 20
Require 10% overlap with respect to the intervals in A:
$ bedtools jaccard -a a.bed -b b.bed -f 0.1
intersection union jaccard n_intersections
5 20 0.25 1
Require 60% overlap with respect to the intervals in A:
$ bedtools jaccard -a a.bed -b b.bed -f 0.6
intersection union jaccard n_intersections
0 25 0.25 0
