bpp-seq Documentation
- This library provides classes to store and analyse biological sequences. Each position in a sequences is coded by a int. An object implementing the bpp::Alphabet interface is used to make the relation between the int code and its more common character representation. Support for DNA, RNA, protein and codon sequences is provided. The bpp::AlphabetTools provides tools to deal with Alphabet objects. The basic bpp::Sequence class contains the code sequence, a name for the sequence and optionally comments. More elaborated classes can be built by inheriting this class. The bpp::SequenceTools static class provides simple analysis tools, like base frequencies measures, concatenation, etc.
- SeqLib also provides tools to perform in silico molecular biology, like complementation, transcription, translation, etc. All these methods are particular cases of alphabet translation, and are implemented via the interface bpp::Translator. Of particular interest are the classes bpp::NucleicAcidsReplication, bpp::DNAToRNA and bpp::GeneticCode + derivatives.
- Sequence collections are stored as containers. The simplest container implements the bpp::SequenceContainer interface, providing access to sequences by their name. The bpp::OrderedSequenceContainer adds access by position in the container. The simplest implementation of this interface is the bpp::VectorSequenceContainer, which stores the sequences as a vector of bpp::Sequence objects (or instances inheriting from this class). Input/output from various file formats is provided, including fasta (bpp::Fasta), GenBank (bpp::GenBank) and Mase (bpp::Mase). Tools dealing with containers can be found in the bpp::SequenceContainerTools static class.
- Support for alignments is provided via the bpp::SiteContainer interface, which enables site access. Sites are stored as a distinct class, similar to a "vertical" sequence, called bpp::Site. It shares several methods with the bpp::Sequence object, although it does not contain a name but a position attribute. This attribute can be used to track the position of sites when handling alignments (for instance after removing all gap-containing sites). There are currently two implementations of the bpp::SiteContainer interface:
- bpp::AlignedSequenceContainer, inheriting from bpp::VectorSequenceContainer and adding the site access. Sequence access is hence in
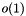 and site access in
and site access in 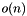 , n being the total number of sites.
, n being the total number of sites. - bpp::VectorSiteContainer is a symmetric implementation, storing the data as a vector of bpp::Site objects, providing site access in
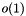 but sequence access in
but sequence access in 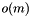 , m being the total number of sequences. The static classes bpp::SiteTools and bpp::SiteContainerTools provide some tools (for instance: pairwise alignment) to deal respectively with bpp::Site and bpp::SiteContainer objects. I/O is provided for several formats, including Clustal (bpp::Clustal) and Phylip (bpp::Phylip).
, m being the total number of sequences. The static classes bpp::SiteTools and bpp::SiteContainerTools provide some tools (for instance: pairwise alignment) to deal respectively with bpp::Site and bpp::SiteContainer objects. I/O is provided for several formats, including Clustal (bpp::Clustal) and Phylip (bpp::Phylip).
- bpp::AlignedSequenceContainer, inheriting from bpp::VectorSequenceContainer and adding the site access. Sequence access is hence in
- Bio++ SeqLib also contains support for sequence properties, like amino-acids biochemical properties. The interfaces bpp::AlphabetIndex1 and bpp::AlphabetIndex2 provides methods to deal with indices in 1 and 2 dimensions respectively. Several basic properties are provided, together with input from the AAIndex databases.
