merge¶
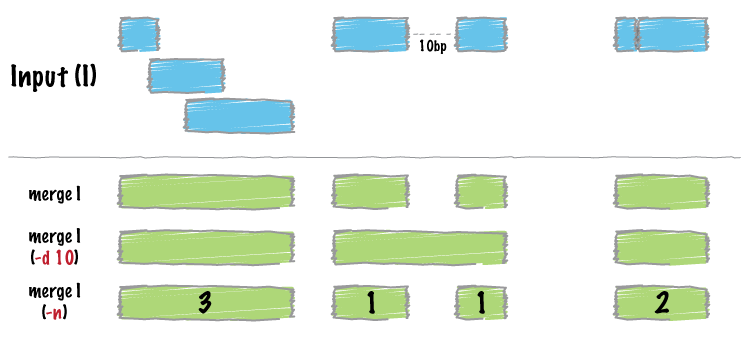
bedtools merge combines overlapping or "book-ended" features in an interval
file into a single feature which spans all of the combined features.
Note
bedtools merge requires that you presort your data by chromosome and
then by start position (e.g., sort -k1,1 -k2,2n in.bed > in.sorted.bed
for BED files).
See also
Usage and option summary¶
Usage:
bedtools merge [OPTIONS] -i <BED/GFF/VCF/BAM>
(or):
mergeBed [OPTIONS] -i <BED/GFF/VCF/BAM>
Option |
Description |
|---|---|
-s |
Force strandedness. That is, only merge features that are the same strand. By default, this is disabled. |
-S |
Force merge for one specific strand only. Follow with + or - to force merge from only the forward or reverse strand, respectively. By default, merging is done without respect to strand. |
-d |
Maximum distance between features allowed for features to be merged. Default is 0. That is, overlapping and/or book-ended features are merged. |
-c |
Specify columns from the input file to operate upon (see -o option, below). Multiple columns can be specified in a comma-delimited list. |
-o |
Specify the operation that should be applied to
-c.Valid operations:
sum, min, max, absmin, absmax,
mean, median,
collapse (i.e., print a delimited list (duplicates allowed)),
distinct (i.e., print a delimited list (NO duplicates allowed)),
count
count_distinct (i.e., a count of the unique values in the column),
Default: sum
Multiple operations can be specified in a comma-delimited list.
If there is only column, but multiple operations, all operations will be
applied on that column. Likewise, if there is only one operation, but
multiple columns, that operation will be applied to all columns.
Otherwise, the number of columns must match the the number of operations,
and will be applied in respective order.
E.g.,
-c 5,4,6 -o sum,mean,count will give the sum of column 5,the mean of column 4, and the count of column 6.
The order of output columns will match the ordering given in the command.
|
-header |
Print the header from the A file prior to results.
|
-delim |
Specify a custom delimiter for the -nms and -scores concat options
Example:
-delim "|"Default: ";" |
Default behavior¶
By default, bedtools merge combines overlapping (by at least 1 bp) and/or
bookended intervals into a single, "flattened" or "merged" interval.
$ cat A.bed
chr1 100 200
chr1 180 250
chr1 250 500
chr1 501 1000
$ bedtools merge -i A.bed
chr1 100 500
chr1 501 1000
-s Enforcing "strandedness"¶
The -s option will only merge intervals that are overlapping/bookended
and are on the same strand.
$ cat A.bed
chr1 100 200 a1 1 +
chr1 180 250 a2 2 +
chr1 250 500 a3 3 -
chr1 501 1000 a4 4 +
$ bedtools merge -i A.bed -s
chr1 100 250
chr1 501 1000
chr1 250 500
To also report the strand, you could use the -c and -o operators (see below for more details):
$ bedtools merge -i A.bed -s -c 6 -o distinct
chr1 100 250 +
chr1 501 1000 +
-S Reporting merged intervals on a specific strand.¶
The -S option will only merge intervals for a specific strand. For example,
to only report merged intervals on the "+" strand:
$ cat A.bed
chr1 100 200 a1 1 +
chr1 180 250 a2 2 +
chr1 250 500 a3 3 -
chr1 501 1000 a4 4 +
$ bedtools merge -i A.bed -S +
chr1 100 250
chr1 501 1000
To also report the strand, you could use the -c and -o operators (see below for more details):
$ bedtools merge -i A.bed -S + -c 6 -o distinct
chr1 100 250 +
chr1 501 1000 +
-d Controlling how close two features must be in order to merge¶
By default, only overlapping or book-ended features are combined into a new
feature. However, one can force merge to combine more distant features
with the -d option. For example, were one to set -d to 1000, any
features that overlap or are within 1000 base pairs of one another will be
combined.
$ cat A.bed
chr1 100 200
chr1 501 1000
$ bedtools merge -i A.bed
chr1 100 200
chr1 501 1000
$ bedtools merge -i A.bed -d 1000
chr1 100 200 1000
-c and -o Applying operations to columns from merged intervals.¶
When merging intervals, we often want to summarize or keep track of the
values observed in specific columns (e.g., the feature name or score) from
the original, unmerged intervals. When used together, the -c and -o
options allow one to select specific columns (-c) and apply operation
(-o) to each column. The result will be appended to the default, merged
interval output. For example, one could use the following to report the
count of intervals that we merged in each resulting interval (this replaces
the -n option that existed prior to version 2.20.0).
$ cat A.bed
chr1 100 200
chr1 180 250
chr1 250 500
chr1 501 1000
$ bedtools merge -i A.bed -c 1 -o count
chr1 100 500 3
chr1 501 1000 1
We could also use these options to report the mean of the score (#5) field:
$ cat A.bed
chr1 100 200 a1 1 +
chr1 180 250 a2 2 +
chr1 250 500 a3 3 -
chr1 501 1000 a4 4 +
$ bedtools merge -i A.bed -c 5 -o mean
chr1 100 500 2
chr1 501 1000 4
Let's get fancy and report the mean, min, and max of the score column:
$ bedtools merge -i A.bed -c 5 -o mean,min,max
chr1 100 500 2 1 3
chr1 501 1000 4 4 4
Let's also report a comma-separated list of the strands:
$ bedtools merge -i A.bed -c 5,5,5,6 -o mean,min,max,collapse
chr1 100 500 2 1 3 +,+,-
chr1 501 1000 4 4 4 +
Hopefully this provides a clear picture of what can be done.
-n Reporting the number of features that were merged¶
Deprecated since version 2.20.0.
See the -c and -o operators.
-nms Reporting the names of the features that were merged¶
Deprecated since version 2.20.0.
See the -c and -o operators.
-scores Reporting the scores of the features that were merged¶
Deprecated since version 2.20.0.
See the -c and -o operators.
-delim Change the delimiter for -c and -o¶
One can override the use of a comma as the delimiter for the -c and
-o collapse|distinct options via the use of the -delim option.
$ cat A.bed
chr1 100 200 A1
chr1 150 300 A2
chr1 250 500 A3
Compare:
$ bedtools merge -i A.bed -c 4 -o collapse
chr1 100 500 A1,A2,A3
to:
$ bedtools merge -i A.bed -c 4 -o collapse -delim "|"
chr1 100 500 A1|A2|A3
