shuffle¶
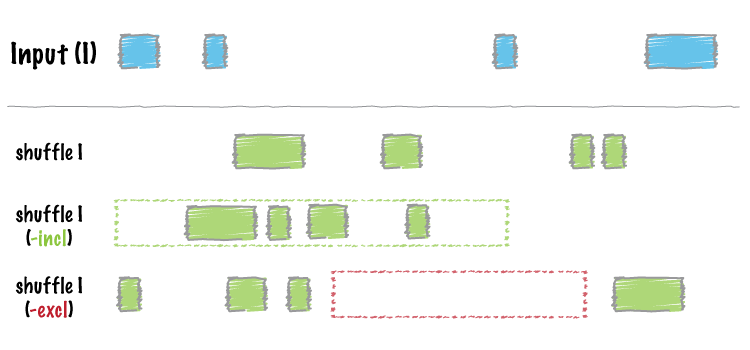
bedtools shuffle will randomly permute the genomic locations of a feature file among a genome defined in a genome file. One can also provide an "exclusions" BED/GFF/VCF file that lists regions where you do not want the permuted features to be placed. For example, one might want to prevent features from being placed in known genome gaps. shuffle is useful as a null basis against which to test the significance of associations of one feature with another.
Usage and option summary¶
Usage:
bedtools shuffle [OPTIONS] -i <BED/GFF/VCF> -g <GENOME>
(or):
shuffleBed [OPTIONS] -i <BED/GFF/VCF> -g <GENOME>
Option |
Description |
|---|---|
-excl |
A BED file of coordinates in which features from -i should not be placed (e.g., genome gaps). |
-incl |
A BED file of coordinates in which features from -i should be placed. |
-chrom |
Keep features in -i on the same chromosome. Solely permute their location on the chromosome. By default, both the chromosome and position are randomly chosen. |
-seed |
Supply an integer seed for the shuffling. This will allow feature shuffling experiments to be recreated exactly as the seed for the pseudo-random number generation will be constant. By default, the seed is chosen automatically. |
-f |
Maximum overlap (as a fraction of the |
-chromFirst |
Instead of choosing a position randomly among the entire genome (the default), first choose a chrom randomly, and then choose a random start coordinate on that chrom. This leads to features being ~uniformly distributed among the chroms, as opposed to features being distribute as a function of chrom size. |
-bedpe |
Indicate that the A file is in BEDPE format. |
-maxTries |
Max. number of attempts to find a home for a shuffled interval in the presence of -incl or -excl. Default = 1000. |
-noOverlapping |
Don't allow shuffled intervals to overlap. |
-allowBeyondChromEnd |
Allow the original the length of the original records to extend beyond the length of the chromosome. |
Default behavior¶
By default, bedtools shuffle will reposition each feature in the input BED file on a random chromosome at a random position. The size and strand of each feature are preserved.
For example:
$ cat A.bed
chr1 0 100 a1 1 +
chr1 0 1000 a2 2 -
$ cat my.genome
chr1 10000
chr2 8000
chr3 5000
chr4 2000
$ bedtools shuffle -i A.bed -g my.genome
chr4 1498 1598 a1 1 +
chr3 2156 3156 a2 2 -
-chrom Requiring that features be shuffled on the same chromosome¶
The -chrom option behaves the same as the default behavior except that features are randomly placed on the same chromosome as defined in the BED file.
$ cat A.bed
chr1 0 100 a1 1 +
chr1 0 1000 a2 2 -
$ cat my.genome
chr1 10000
chr2 8000
chr3 5000
chr4 2000
$ bedtools shuffle -i A.bed -g my.genome -chrom
chr1 9560 9660 a1 1 +
chr1 7258 8258 a2 2 -
-excl Excluding certain genome regions from bedtools shuffle¶
One may want to prevent BED features from being placed in certain regions of
the genome. For example, one may want to exclude genome gaps from permutation
experiment. The excl option defines a BED file of regions that should be
excluded. bedtools shuffle will attempt to permute the locations of all features
while adhering to the exclusion rules. However it will stop looking for an
appropriate location if it cannot find a valid spot for a feature
after 1,000,000 tries.
For example (note that the exclude file excludes all but 100 base pairs of the chromosome):
$ cat A.bed
chr1 0 100 a1 1 +
chr1 0 1000 a2 2 -
$ cat my.genome
chr1 10000
$ cat exclude.bed
chr1 100 10000
$ bedtools shuffle -i A.bed -g my.genome -excl exclude.bed
chr1 0 100 a1 1 +
Error, line 2: tried 1000000 potential loci for entry, but could not avoid excluded
regions. Ignoring entry and moving on.
For example (now the exclusion file only excludes the first 100 bases of the chromosome):
$ cat A.bed
chr1 0 100 a1 1 +
chr1 0 1000 a2 2 -
$ cat my.genome
chr1 10000
$ cat exclude.bed
chr1 0 100
$ bedtools shuffle -i A.bed -g my.genome -excl exclude.bed
chr1 147 247 a1 1 +
chr1 2441 3441 a2 2 -
-seed Defining a "seed" for the random replacement.¶
bedtools shuffle uses a pseudo-random number generator to permute the locations of BED features. Therefore, each run should produce a different result. This can be problematic if one wants to exactly recreate an experiment. By using the seed option, one can supply a custom integer seed for bedtools shuffle. In turn, each execution of bedtools shuffle with the same seed and input files should produce identical results.
For example (note that the exclude file below excludes all but 100 base pairs of the chromosome):
$ cat A.bed
chr1 0 100 a1 1 +
chr1 0 1000 a2 2 -
$ cat my.genome
chr1 10000
$ bedtools shuffle -i A.bed -g my.genome -seed 927442958
chr1 6177 6277 a1 1 +
chr1 8119 9119 a2 2 -
$ bedtools shuffle -i A.bed -g my.genome -seed 927442958
chr1 6177 6277 a1 1 +
chr1 8119 9119 a2 2 -
. . .
$ bedtools shuffle -i A.bed -g my.genome -seed 927442958
chr1 6177 6277 a1 1 +
chr1 8119 9119 a2 2 -
-noOverlapping Prevent shuffled intervals from overlapping.¶
There often arise cases where one wants to shuffle intervals throughout
the genome, yet one wants to prevent the intervals from occupying a single
common base pair. The -noOverlapping option allows one to enforce
no such overlaps.
$ bedtools shuffle -i A.bed -g my.genome -noOverlapping
-allowBeyondChromEnd Allow records to extend beyond the chrom. length.¶
By default, shuffle requires that an interval's original length must be
fully-contained within the chromosome. Yet there are cases where you might
want to allow shuffled intervals to be relocated to a position
in which the entire original interval cannot fit w/o exceeding
the end of the chromosome. By using the -noOverlapping option,
shuffle will allow intervals to be shuffled to locations that are so close
to the chromosome end that the full length of the original record cannot
be contained within the chromosome length. In such cases, the end coordinate
for the shuffled interval will be set (i.e., truncated)
to the chromosome's length.
$ bedtools shuffle -i A.bed -g my.genome -allowBeyondChromEnd
